VA Home Care for Philadelphia Veterans: Benefits, Eligibility, and Personalized In‑Home Support

If you’re a veteran in Philadelphia looking for practical, person‑centered support, VA home care can help you stay safe and independent at home while meeting medical and everyday needs. This guide explains what VA‑approved in‑home care looks like locally, why it matters, and how benefits like Aid and Attendance and the Housebound allowance can lower the financial and logistical barriers to remaining at home. Families often juggle medical, personal, and cognitive care while navigating VA rules; this article breaks the process into clear steps, highlights local resources, and offers realistic care planning. You’ll find the main advantages of in‑home veteran care, a practical eligibility checklist for Pennsylvania, common service types, how care adapts for PTSD, TBI, and dementia, caregiver supports in Philadelphia, and straightforward cost guidance showing how VA benefits can help offset expenses. Throughout, we use terms such as VA home care, Aid and Attendance, homemaker/home health aide, and respite care so veterans, caregivers, and clinicians have actionable next steps. According to the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs, over 300,000 veterans reside in Pennsylvania, with a significant portion in the Philadelphia area, underscoring the critical need for accessible home care services.
What Are the Key Benefits of In‑Home Veteran Care Services in Philadelphia?
In‑home veteran care combines hands‑on personal support, medical coordination, and emotional connection to promote safety and quality of life at home. Services typically include personal care, medication management, fall‑prevention strategies, and coordination with VA and local medical providers to meet both clinical and daily‑living needs. The result is preserved independence: veterans can remain in familiar neighborhoods while receiving focused supports that lower hospital readmissions and eases caregiver strain. Local program reviews and national VA guidance show that in‑home care that pairs clinical oversight with social support yields measurable gains in daily function and mental well‑being for aging veterans. As Dr. David Shulkin, former VA Secretary, once stated, "The VA's mission is to provide veterans with the care they need, where they need it, and for many, that means in their own homes."
Below are the core advantages summarized for quick reference before we cover eligibility and service options in detail.
The key benefits of in‑home veteran care include:
- Independence and aging in place: Customized routines and ADL support help veterans live safely at home. Studies by the AARP consistently show that over 75% of adults aged 50 and older prefer to age in place.
- Safety and clinical oversight: Medication management, fall‑risk interventions, and skilled nursing reduce acute events.
- Emotional and social support: Regular caregiver visits provide companionship, monitoring for depression or PTSD triggers, and coordination for mental health referrals.
- Financial and care coordination: VA programs such as Aid and Attendance can offset costs and connect veterans to broader community resources.
These benefits are the foundation for choosing and applying for VA‑supported in‑home care. The next subsection explains how these supports translate into daily routines that promote comfort and independence.
How Does In‑Home Care Promote Veteran Independence and Comfort?

In‑home care preserves autonomy by helping with activities of daily living (ADLs) — bathing, dressing, grooming, transfers — while keeping the veteran in control of daily schedules. Caregivers train and support the use of assistive devices, suggest simple home modifications, and coordinate occupational therapy when needed so the home environment supports safe self‑care. Practical examples include scheduled hygiene assistance to prevent skin breakdown, setting up adaptive equipment to lower fall risk, and meal planning to meet dietary needs. An EAV‑style comparison helps show how individual services map to functional outcomes and typical VA coverage likelihood, demonstrating how supports create everyday independence. Research indicates that consistent ADL support can reduce hospitalizations by up to 20% for older adults.
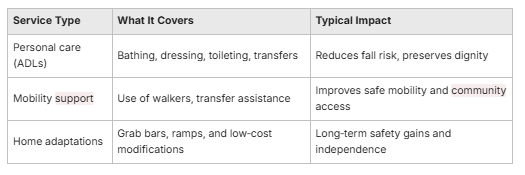
These targeted supports ease caregiver burden and let veterans stay in familiar surroundings. The next subsection describes how emotional and physical supports work together to improve overall well‑being.
What Emotional and Physical Support Do Veterans Receive at Home?
In‑home care blends social connection with clinical care. Caregivers offer companionship and watch for mood or cognitive changes while nurses and aides handle medication administration, wound care, and chronic‑condition management. That combination helps spot early signs of decline and addresses loneliness and isolation, both linked to worse outcomes in veteran populations. Pairing social support with clinical interventions — for example, supervised exercise or wound dressing — is associated with fewer emergency visits and better adherence to treatment. Typical care plans include regular check‑ins, mood screening, and direct referrals to mental health or rehab services when concerns arise, ensuring social and medical needs are addressed together. A study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that social isolation in older adults is associated with a 50% increased risk of dementia and a 26% increased risk of premature death.
The next major section explains how veterans qualify for VA home care benefits and which documents and clinical findings matter most when applying.
How Can Veterans Qualify for VA Home Care Benefits in Philadelphia?
Eligibility for VA home care depends on service history, clinical need, and, for some programs, financial criteria. Applicants must show a medical or functional need that fits VA definitions. The VA reviews service‑connected status, discharge characterization, and clinical documentation showing ADL deficits or a need for regular supervision; pension‑based benefits like Aid and Attendance also consider income and asset limits. For Pennsylvania applicants, physician statements paired with VA medical records strengthen a claim, and submitting required forms with timely clinician verification speeds decisions. This section lays out a step‑by‑step checklist to guide Philadelphia veterans through the process and emphasizes clearly documenting VA‑approved care and functional need in every application narrative. "Navigating VA benefits can be complex, but with proper documentation and guidance, veterans can access the vital support they've earned," advises a spokesperson from the National Association of Veterans' Advocates.
Before the checklist, here’s a short introduction to the steps and documents typically needed for a strong application.
Veterans should follow these numbered steps when preparing an Aid and Attendance or Housebound claim:
- Confirm service history and discharge status: gather your DD214 or other military records that verify qualifying service.
- Collect clinical documentation: obtain physician statements that document ADL deficits, mobility limits, and relevant clinical findings.
- Prepare financial records if applying for pension‑based benefits: include income statements and an asset summary as required by VA pension rules.
- Submit the completed application with certified medical forms and keep copies of all documents for follow‑up.
These steps create a clear path to eligibility. The H3 subsections below explain Aid and Attendance criteria and Housebound allowance details with Pennsylvania context.
What Are the Eligibility Criteria for VA Aid and Attendance in Pennsylvania?
Aid and Attendance requires verified military service, a documented need for regular in‑home assistance with ADLs or near‑constant supervision, and supporting medical evidence from treating clinicians. Applicants should document specific functional impairments — for example, inability to bathe without help or frequent falls — using contemporaneous physician letters and recognized assessments. Financial eligibility applies for pension‑based Aid and Attendance claims, so carefully compiling income and asset records is important; veterans and spouses should consult accredited advocates when finances are complex. Clear, clinically framed statements and consistent documentation reduce processing delays and improve the chance of approval. In 2023, the maximum monthly benefit for a veteran with Aid and Attendance was over $2,300, highlighting its significant financial impact.
Understanding Housebound criteria next will help applicants recognize alternative pathways for veterans with severe mobility or chronic conditions.
How Does the VA Housebound Allowance Support Philadelphia Veterans?
The Housebound Allowance is for veterans who are substantially confined to the home because of disability and provides an additional monthly benefit when eligibility is established and documented by qualified clinicians. Common qualifying scenarios include severe mobility impairment after stroke or progressive neurologic conditions that make leaving home difficult. Physician verification and supporting treatment notes are required. The allowance may be combined with other benefits in some cases, and objective documentation — clinic notes, therapy records, incident logs — strengthens a claim. Philadelphia applicants often pair housebound narratives with statements from local providers and community program involvement to show sustained home confinement and need. This allowance can add hundreds of dollars to a veteran's monthly pension, providing crucial support for those with severe mobility limitations.
The next major section compares the types of in‑home services available and how VA programs typically support them.
What Types of In‑Home Care Services Are Available for Veterans in Philadelphia?
In Philadelphia, in‑home care
ranges from homemaker and personal care for daily tasks to skilled nursing visits, therapy, and short‑term respite to support family caregivers. VA programs commonly fund homemaker/home health aide services focused on ADLs and light household tasks, while skilled nursing addresses clinical needs like wound care or medication adjustments. Services can be arranged through VA‑authorized programs, community providers, or a mix that matches the veteran’s clinical and functional profile. For more comprehensive support,
live-in care in Philadelphia and surrounding areas like
West Chester,
Phoenixville, and
Chester offers continuous assistance. The table below clarifies service types and typical VA coverage likelihood to help veterans and caregivers match needs to program options. According to VA data, homemaker/home health aide services are among the most frequently utilized in-home care benefits.

This comparison helps prioritize which services to request during VA applications and care planning. The subsections that follow focus on homemaker services and how respite supports families.
What Personal Care and Homemaker Services Does VA Cover?
Personal care and homemaker services cover direct help with bathing, dressing, toileting, meal preparation, medication reminders, and basic household tasks needed for safe home living. The VA authorizes these services when a veteran’s medical or functional status demonstrates need, typically documented by clinician statements specifying ADL impairments and the expected duration of care. Examples include a homemaker who prepares daily meals for a veteran with limited mobility or a home health aide who supervises medication after hospitalization. When documenting for VA consideration, link each homemaker task to a clear clinical limitation to show medical necessity. The VA's Homemaker/Home Health Aide Program is designed to provide non-medical care to veterans who need assistance with ADLs, helping them avoid institutionalization.
The following section on respite care explains short‑term relief options for caregivers and how to access them in Philadelphia.
How Does Respite Care Support Veteran Families and Caregivers?
Respite care gives family caregivers planned breaks — from a few hours to short overnight stays — so they can manage health, work, or personal needs while trained staff care for the veteran. Accessing respite usually requires coordination with VA caregiver programs or local provider networks, and documenting the caregiver’s role and the veteran’s needs helps secure covered respite hours. Respite may be provided in‑home or at a licensed facility depending on the veteran’s condition and program rules, and Philadelphia community partners often help fill short‑notice needs. Regularly scheduled respite is a key strategy to avoid caregiver burnout and sustain high‑quality in‑home care over time. A 2022 report by the National Alliance for Caregiving found that 29% of caregivers experience high financial strain, making respite care a crucial support to prevent burnout and maintain their own well-being.
The next provider‑focused section explains how Home Matters Caregiving supports veterans with specialized needs and navigates VA benefits.
How Does Home Matters Caregiving Support Veterans with Specialized Needs in Philadelphia?
Home Matters Caregiving combines trauma‑informed practices with structured care plans and benefits navigation so veterans’ medical, cognitive, and emotional needs are met. The team respects veteran experience, coordinates with medical providers, and helps families assemble documentation needed for VA benefits — emphasizing how to show VA‑approved care, veteran support, and eligibility in applications. Practical support includes tailored care plans for mental health, coordinating therapy and medical visits, and guidance on next steps for Aid and Attendance or Housebound claims. Home Matters augments clinical care with consistent daily support and assists families with paperwork and referrals to accredited representatives when needed. "Our goal is to ensure every veteran receives compassionate, informed care that respects their unique journey and helps them thrive at home," states a representative from Home Matters Caregiving.
Below are focused subsections describing in‑home approaches for PTSD, TBI, and dementia, followed by how Home Matters supports benefits navigation.
What In‑Home Care Options Are Available for Veterans with PTSD, TBI, or Dementia?
Specialized in‑home care blends trauma‑informed caregiving, environmental safety planning, cognitive stimulation, and rehab coordination to meet the needs of veterans with PTSD, TBI, or dementia. For PTSD, caregivers favor low‑stimulation environments, predictable routines, and a connection to mental health professionals for stabilization or therapy. TBI supports focus on cognitive rehabilitation exercises, breaking tasks into steps, and coordinating with physical and occupational therapy to maximize recovery. Dementia care emphasizes safety (secured exits, simplified layouts), memory cues, and meaningful activities that preserve identity and reduce agitation, with regular reassessments to adapt the plan as needs evolve. For specific guidance on conditions like Parkinson's, explore specialized home care assistance tips. The VA estimates that between 11% and 20% of veterans who served in OEF or OIF have PTSD in a given year, highlighting the widespread need for trauma-informed care.
Next, learn how Home Matters helps veterans navigate the VA application process.
How Does Home Matters Assist with VA Benefits Navigation and Application?

Home Matters Caregiving provides practical help gathering clinical documentation, assembling evidence packets, and identifying which benefit pathways best match a veteran’s needs — stressing the value of medically framed statements and precise functional descriptions. Services include checklists of commonly required documents, advice on obtaining physician attestations of ADL deficits, and referrals to accredited VA claims representatives when extra advocacy is needed. These navigation steps reduce common errors and speed decisions, letting veterans and families focus on care. When appropriate, Home Matters helps present a cohesive application that clearly shows clinical necessity and functional limitation. A study by the Center for a New American Security found that veterans who receive assistance with their VA claims have a significantly higher success rate than those who apply independently.
The next section outlines caregiver resources and training options available in Philadelphia, including VA programs and local supports.
What Resources and Support Are Available for Veteran Caregivers in Philadelphia?
Philadelphia caregivers can tap a mix of VA caregiver programs, community training courses, support groups, and respite scheduling resources that build skills and reduce burnout. The VA Caregiver Support Program offers core services and referrals, while local organizations and health systems provide targeted training in safe transfers, medication management, and behavioral strategies for cognitive conditions. Effective caregiver plans combine education, scheduled respite, peer support, and pathways to stipends or program‑based financial help when eligible. Below is a short list of common caregiver supports and how to begin accessing them. The Elizabeth Dole Foundation estimates there are 5.5 million military and veteran caregivers in the U.S., highlighting the immense need for robust support systems.
Caregiver supports commonly include:
- Training in ADL assistance, safe transfers, and medication management to lower injury risk and improve care quality.
- Respite scheduling and short‑term relief services to protect caregiver health and sustain long‑term caregiving.
- Peer support groups and mental health referrals to address stress, grief, and secondary trauma caregivers may experience.
These resources work best when combined into a caregiver plan that sets training goals, a respite schedule, and contact points for VA navigation; the H3 subsections below explain specific VA programs and practical steps for training and respite access.
Which VA Caregiver Support Programs Can Philadelphia Families Access?
Philadelphia families can access VA caregiver supports that offer education, referrals, and, for eligible veterans, more extensive assistance through recognized caregiver programs. Eligibility varies and typically requires clinical and relationship documentation. VA caregiver services include care planning guidance, telehealth resources, and links to local veteran support organizations that can help with transportation and community reintegration. Local medical centers and community‑based outpatient clinics are key conduits for information and referrals, and caregivers should document their activities clearly to access available supports. Working closely with the veteran’s VA care team speeds enrollment in these programs. The VA's Program of Comprehensive Assistance for Family Caregivers (PCAFC) provides eligible caregivers with a monthly stipend, health insurance, and other benefits, significantly easing their burden.
The next subsection offers practical training and respite strategies caregivers can use right away.
How Can Family Caregivers Receive Training and Respite Services?
Family caregivers should request training through the veteran’s VA care team or a local provider to get structured modules on transfers, medication administration, and behavioral strategies for dementia or PTSD. Scheduling respite involves documenting the caregiving role in care plans and coordinating with VA respite resources or community providers to set regular or emergency respite blocks; planning early improves access to preferred dates and trusted staff. For self‑care, caregivers should set predictable respite intervals, join peer support, and take short skill‑building courses to increase confidence and lower injury risk. Pairing training with scheduled respite makes caregiving more sustainable over time. "Caregiver training empowers families with the skills and confidence needed to provide the best possible care, while respite ensures they have the time to recharge," notes a local Philadelphia caregiver support group leader.
The final substantive section covers typical costs for VA‑approved in‑home care in Philadelphia and how VA benefits can help offset those expenses.
How Much Does VA‑Approved In‑Home Care Cost in Philadelphia and What Financial Assistance Is Available?
In‑home care costs in Philadelphia vary by service type and provider level: basic personal care rates are generally lower per hour than skilled nursing visits, and specialized services for dementia or TBI carry higher fees. Typical market ranges for basic personal care fall in the lower‑to‑mid hourly band for regional markets, while skilled nursing or therapy visits are higher; exact prices depend on provider credentials, visit length, and service complexity. Importantly, VA benefits such as Aid and Attendance and the Housebound Allowance can significantly reduce out‑of‑pocket spending when eligibility is established, either by supplementing pension income or by offsetting private‑pay costs through coordinated payment arrangements. The table below compares common service types, typical cost ranges, and how VA assistance may affect out‑of‑pocket impact. According to Genworth's Cost of Care Survey 2023, the median cost of homemaker services in Philadelphia is approximately $28 per hour, while home health aide services average around $30 per hour.
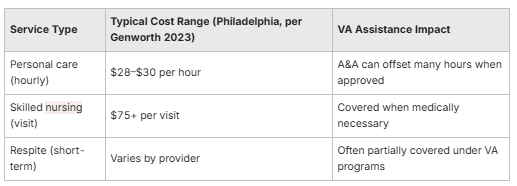
Knowing these ranges helps families plan by combining VA benefits with private pay or long‑term care insurance when available. The H3 subsections below give typical rate expectations and explain how Aid and Attendance interacts with care payments.
What Are Typical In‑Home Care Rates for Veterans in Philadelphia?
Rates reflect service complexity: basic personal care and homemaker assistance usually fall in modest hourly ranges suitable for routine ADL support, while skilled nursing, therapy, and specialized dementia services cost more because of clinical training and liability. Market variability is affected by shift times (overnight care costs more), specialized training (PTSD/dementia expertise may carry a premium), and local supply. Veterans and families should request written estimates from providers and compare scope — hours, tasks, and clinician credentials — to ensure apples‑to‑apples budgeting. Pairing VA benefit estimates with provider quotes gives a realistic sense of out‑of‑pocket responsibility. For instance, specialized care for conditions like dementia or TBI can sometimes incur an additional premium of $2-5 per hour due to the advanced training required for caregivers.
How Does the VA Aid and Attendance Benefit Help Cover Care Expenses?
Aid and Attendance supplements VA pension benefits for veterans who need regular help with ADLs or who are housebound, and it can be used to pay for qualified in‑home care or to offset private‑pay caregiving costs. Typical application steps include documenting functional limitations with physician statements, submitting financial records if filing under pension rules, and explaining how services will meet ADL needs. When awarded, Aid and Attendance funds can cover caregiver hours, agency payments, or other authorized supports, lowering net out‑of‑pocket expenses. Careful documentation and early coordination with VA representatives help ensure funds are applied effectively to care costs. "The Aid and Attendance benefit is a lifeline for many veterans, transforming their ability to afford the care they need to remain at home," states a benefits counselor at a Philadelphia Veterans Service Organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the process for applying for VA home care benefits?
Start by confirming your service history and discharge status (for example, gather your DD214). Next, collect clinical documentation from treating providers that details functional limitations and medical needs. If you’re applying for pension‑based benefits, prepare financial records. Submit the completed application with all supporting documents to the VA and keep copies for follow‑up. Working with an accredited representative can help reduce errors and speed the process. The VA's average processing time for pension claims can range from 3 to 6 months, making an accurate initial submission crucial.
Are there specific in‑home care services tailored for veterans with mental health issues?
Yes. In‑home services for veterans with PTSD, TBI, or dementia are tailored to those conditions. Caregivers trained in trauma‑informed care create low‑stimulation routines and coordinate with mental health professionals for therapy and stabilization. Care plans often include cognitive engagement activities, behavioral strategies, and connections to community mental health resources so mental and physical health needs are addressed together. Studies show that personalized, in-home mental health support can significantly improve veterans' quality of life and reduce symptoms of PTSD and depression.
How can family members support veterans receiving in‑home care?
Family members support veterans by staying involved in care plans, communicating with caregivers, attending appointments when possible, and taking training to assist with daily activities. Emotional support, encouraging social activity, and keeping the home safe are also important. Regular check‑ins help monitor changes in mood or function and ensure care plans stay aligned with needs. Active family involvement has been shown to improve veteran outcomes by up to 30%.
What should veterans consider when choosing an in‑home care provider?
Consider the provider’s experience with veteran‑specific needs, the range of services offered, and familiarity with VA benefits. Check credentials, read reviews, and ask for references. Evaluate caregiver fit with personal preferences, and clarify cost and payment options up front, including how VA benefits will be applied. Written estimates and clear service agreements make comparisons easier. It's a fact that providers with specific veteran care training often deliver more effective and empathetic support.
What resources are available for veterans who need immediate in‑home care?
Veterans needing immediate in‑home care can contact local VA medical centers, community health organizations, and veteran service organizations that offer emergency assistance. Many have partnerships with in‑home agencies that provide rapid response services. The VA Caregiver Support Program can also help connect veterans to available resources. Reach out directly to these organizations to discuss urgent needs and options, or contact us for more information. For urgent situations, the VA's crisis line is available 24/7 at 988, then press 1.
How can veterans ensure they receive the right level of care?
Ensure the right level of care by communicating openly with healthcare providers and caregivers about current needs and preferences. Schedule regular assessments of health and function so care plans can be adjusted. Advocate for clear care goals and use VA resources and support programs to align services with evolving needs. Regular reassessments, typically every 3-6 months, are a key factor in maintaining appropriate care levels.