The Role of Occupational Therapy in Alzheimer's Care

Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects older adults, causing cognitive decline, memory loss, and difficulty in performing daily activities. As the prevalence of Alzheimer's continues to rise globally, the importance of effective care strategies becomes paramount. Among these strategies, occupational therapy (OT) plays a crucial role in improving the quality of life for individuals living with Alzheimer's disease. This article delves into the significance of occupational therapy in Alzheimer's care, exploring its various interventions and their impact on patients and caregivers.
Understanding Alzheimer's Disease
Before delving into the role of occupational therapy, it's essential to understand the nature of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, leading to the deterioration of nerve cells and subsequent cognitive impairment. As the disease progresses, individuals may struggle with memory loss, confusion, disorientation, and challenges in performing routine tasks such as dressing, bathing, and eating independently.
What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy is a holistic healthcare profession aimed at helping individuals engage in meaningful activities and occupations that are essential for daily living. OT practitioners work with individuals of all ages and abilities to promote health, well-being, and participation in daily life activities. In the context of Alzheimer's care, occupational therapists focus on maintaining patients' independence and enhancing their quality of life through tailored interventions.
The Role of Occupational Therapy in Alzheimer's Care
Occupational therapy plays a multifaceted role in the care of individuals with Alzheimer's disease, addressing physical, cognitive, emotional, and environmental challenges. Here are some key components of occupational therapy in Alzheimer's care:
Assessment and Evaluation: Occupational therapists conduct comprehensive assessments to evaluate patients' cognitive and functional abilities, as well as their home and community environments. These assessments help identify areas of strength and areas needing support, guiding the development of personalized care plans.
Cognitive Rehabilitation: Cognitive impairment is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, impacting memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Occupational therapists employ various cognitive rehabilitation techniques to help individuals maintain cognitive function and adapt to changes. These may include memory exercises, sequencing tasks, and cognitive strategies to improve attention and executive function.
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Training: Alzheimer's can hinder individuals' ability to perform basic activities of daily living independently. Occupational therapists provide training and support to help patients with tasks such as dressing, grooming, bathing, and feeding. They may also recommend assistive devices or modifications to the home environment to enhance safety and accessibility.
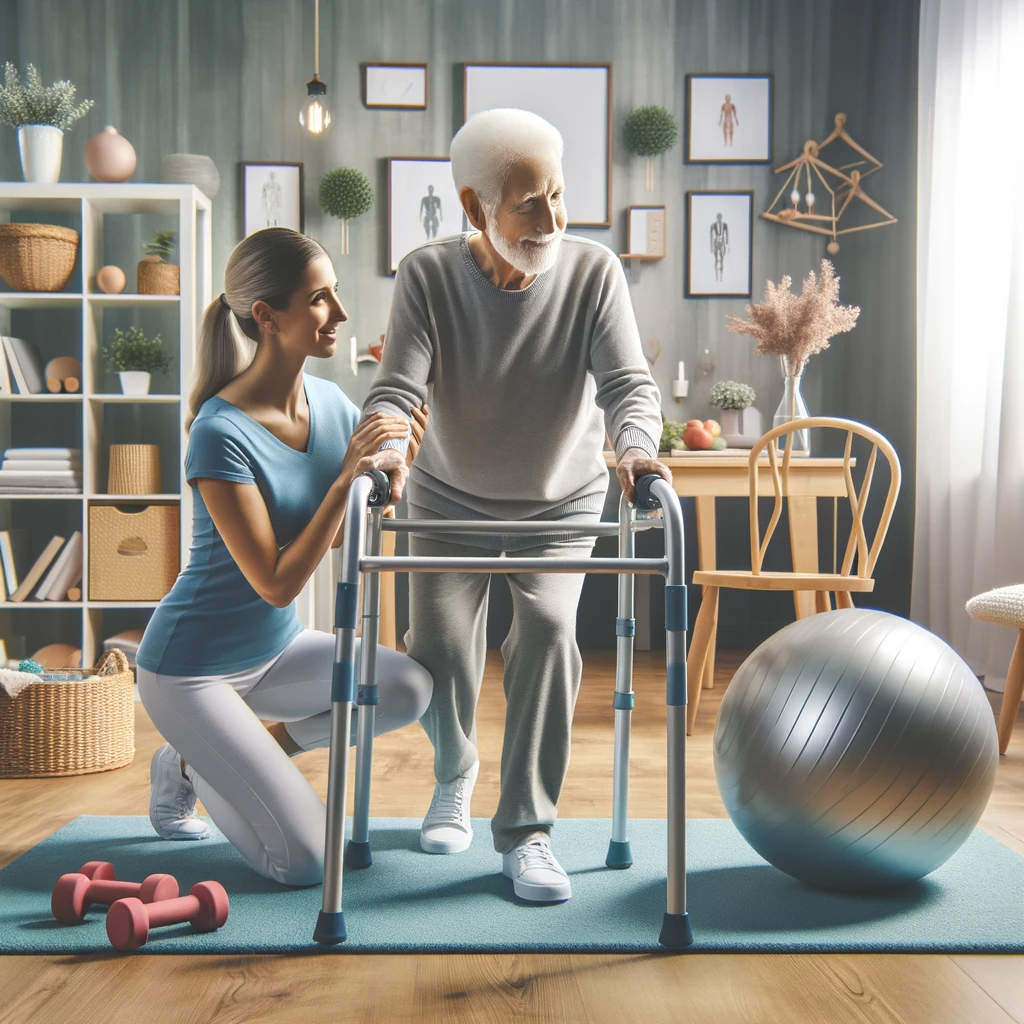
Functional Mobility and Rehabilitation: As Alzheimer's progresses, individuals may experience decline in mobility and motor skills, increasing their risk of falls and injuries. Occupational therapists work on improving balance, strength, and coordination through customized exercise programs and mobility aids. They also educate patients and caregivers on fall prevention strategies and techniques for safe movement.
Sensory Stimulation: Sensory stimulation activities can help individuals with Alzheimer's engage their senses, promote relaxation, and reduce agitation. Occupational therapists may incorporate sensory-based interventions such as aromatherapy, music therapy, tactile stimulation, and multisensory environments to enhance well-being and mood.
Environmental Modifications: Creating a supportive and dementia-friendly environment is essential for optimizing the safety and comfort of individuals with Alzheimer's. Occupational therapists assess home and living spaces to identify potential hazards and recommend modifications such as grab bars, non-slip flooring, simplified layouts, and visual cues to promote independence and reduce confusion.
Caregiver Education and Support: Occupational therapists recognize the vital role of caregivers in Alzheimer's care and provide education, training, and support to help them effectively manage caregiving responsibilities. This may include teaching techniques for communication, behavior management, stress reduction, and self-care, empowering caregivers to navigate the challenges of caring for a loved one with Alzheimer's.
The Impact of Occupational Therapy on Alzheimer's Care
The interventions provided by occupational therapists have a significant impact on the lives of individuals with Alzheimer's disease and their caregivers. By addressing the unique needs and challenges associated with the condition, occupational therapy helps:
Promote Independence: Occupational therapy interventions focus on maximizing patients' independence and autonomy in daily activities, enhancing their sense of dignity and self-worth.
Improve Quality of Life: Through cognitive stimulation, functional training, and environmental modifications, occupational therapy enhances patients' quality of life by enabling them to participate in meaningful activities and maintain social connections.
Reduce Caregiver Burden: By equipping caregivers with practical skills, knowledge, and support, occupational therapy reduces caregiver stress and burnout, fostering a healthier caregiving dynamic and improving overall family well-being.
Delay Institutionalization: By facilitating functional abilities and providing support in the home environment, occupational therapy interventions may help delay the need for institutional care, allowing individuals with Alzheimer's to remain in familiar surroundings for longer.
Enhance Safety and Well-being: Occupational therapists play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals with Alzheimer's by addressing environmental hazards, promoting mobility and independence, and implementing strategies to manage behavioral symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, occupational therapy plays a vital role in Alzheimer's care by addressing the complex needs of individuals living with the disease and their caregivers. Through a holistic approach encompassing cognitive rehabilitation, functional training, environmental modifications, and caregiver support, occupational therapists empower individuals with Alzheimer's to maintain independence, dignity, and quality of life. As the prevalence of Alzheimer's continues to grow, the role of occupational therapy remains indispensable in promoting the health, well-being, and autonomy of those affected by this devastating condition. Contact us today at Home Matters Care giving to learn more about how our occupational therapy services can make a difference in Alzheimer's care.